Cannabinoid or CBD is among the main components of the cannabis plant. In recent years, cannabis is being grown in many states across the U.S., as many researchers are now focusing on its therapeutic benefits. Although most people relate cannabis to the intoxicating element (tetrahydrocannabinol) or THC – CBD doesn’t cause intoxication. However, CBD affects the nervous system and the body.
Researchers are still trying to identify ways to use CBD for both health and wellness. This is after more and more evidence has revealed the numerous advantages of CBD, including improving our health and quality of life. Botanicam
The Endocannabinoid System
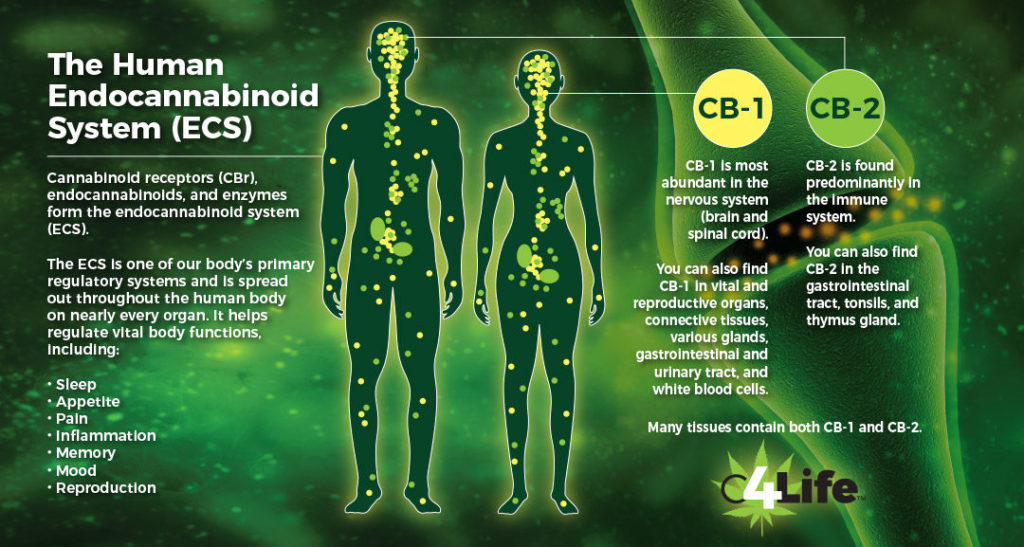
In case you didn’t know, your body produces its own cannabinoids referred to as endocannabinoids. Their primary role in the body is to maintain a well-balanced environment, including body temperature, glucose levels, and pH balance, among others. The endocannabinoids maintain the internal processes despite the external environment like toxins, air quality, the foods we consume, and sun exposure.
If you’re wondering where these endocannabinoids come from, your body has an endocannabinoid system or ECS. This system has two main receptors: CB1 and CB2.
CB1 receptors
The CB1 receptors are mainly concentrated in your nervous system and the brain. According to NCBI, the brain has a higher number of these receptors than all other neurotransmitter receptors. Because of the high concentration of these receptors, their main function is to regulate your movement, mood, emotions, and memories, among others. CB1 receptors can also be found in the connective tissues, some organs, glands, and gonads.
Benefits of CB1 receptors
- Increase myelin formation
- Lowering blood pressure
- Relieve depression
- Lowering anxiety
- Lowering prolactin
- Decrease intestinal permeability or leaky gut syndrome
CB2 receptors
The CB2 receptors in your body are mostly located within your immune system. However, these receptors are also found in other vital organs like the kidneys, heart, and liver.
Additionally, the CB2 receptors are also in your bones, blood vessels, reproductive organs, and lymph nodes. Only a small number of these receptors exist in the brain. The CB2 receptors function in treating almost every type of disease, including gastrointestinal, cardiovascular, psychiatric, neurodegenerative, and autoimmune disorders. It also plays a significant role in kidney and liver functions, cancer, bone and skin health, and pain-related diseases.
How the Endocannabinoid System Works
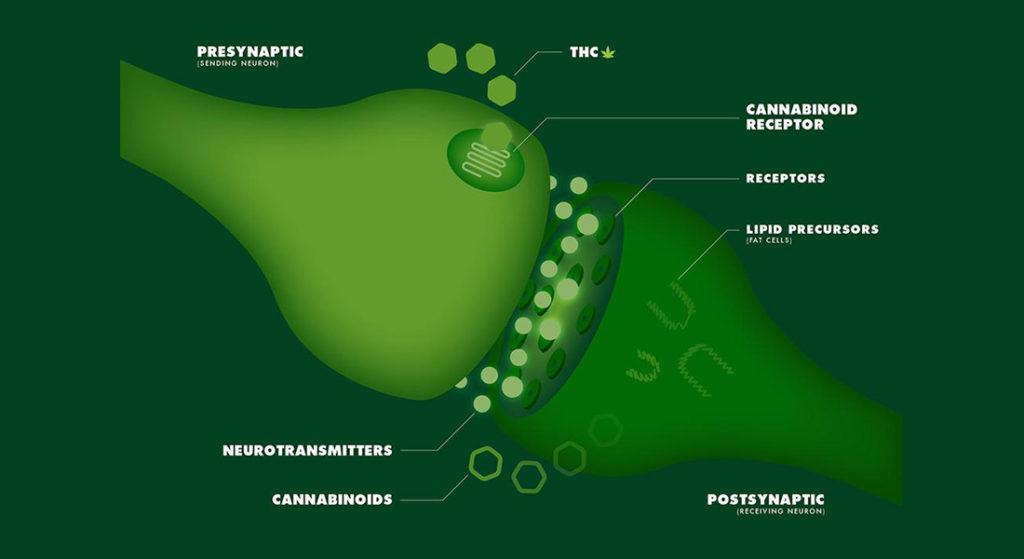
You now know the two types of receptors in the body’s endocannabinoid system, but it’s also important that you understand how the system works in your body.
Because your body’s ECS system is responsible for creating and maintaining various body processes, it kicks in when something malfunctions.
The enzymes in your body create endocannabinoids. These endocannabinoids are then attached to the suitable receptors to stimulate the expected responses. For instance, when you’re hungry, the system produces endocannabinoids that are bonded to the receptors, which are in high numbers in the hypothalamus. These receptors help control your appetite, and they stimulate the normal reactions in your body to indicate that your body needs food. This explains why your stomach growls.
After the endogenous cannabinoids have accomplished their purpose and all processes normalized, the enzymes break them down to inhibit them from repeatedly sending signals.
When the endocannabinoid system is performing appropriately, it impacts the specific thing that is needed to restore balance. However, it only regulates unbalanced systems and leaves those working properly.
How CBD Works Together With Your Body
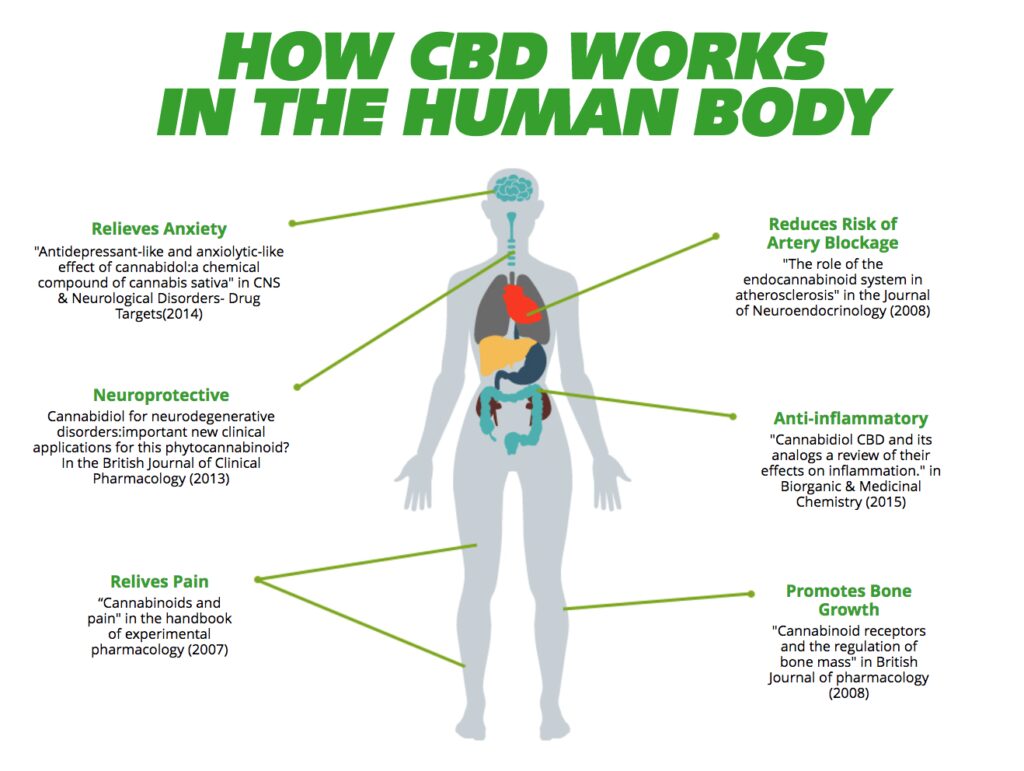
Phytocannabinoids (Cannabinoids extracted from plants) produce cannabinoids similar to those produced by your body. This means they can stimulate and also influence the ECS like the naturally occurring endocannabinoids in your body. However, unlike THC, CBD doesn’t bind itself directly to the body’s endocannabinoid system receptors. The direct bonding with the receptors can cause overstimulation, and this creates the high feeling from THC. Instead, CBD influences your receptors indirectly and stimulates them to restore balance in your body processes.
Apart from interacting with the body’s ECS receptors, CBD also stimulates other receptors in your brain to maintain balance. For instance, it stimulates the serotonin receptors, in particular, the 5-HTIA receptor that helps ease addiction, nausea, pain, sleep disorders, and anxiety. What’s more, it stimulates nuclear receptors in the brain and helps create a similar effect to antidepressants.
Do You Need CBD Even Though Your Body Makes Cannabinoids?

If your body has the ability to make cannabinoids that can also normalize functions independently, you may think using CBD is irrelevant. However, there are several things that can interfere with your endocannabinoid system and inhibit the normal production of endocannabinoids. This may prevent your body from producing enough endocannabinoids to create homeostasis. According to ECHO Connection, the lack of enough endocannabinoids may result in a condition known as endocannabinoid deficiency.
If your body has an endocannabinoid deficiency and it is unable to regulate processes properly, you can easily get ill or develop diseases. Your system may also get some issues like irritable bowel syndrome, motor issues like Parkinson’s disease, cognitive disorders like Alzheimer’s disease, and mental disorders (migraines). In a recent report by the National Institute of Health, manipulating your ECS by introducing phytocannabinoids like CBD can help to efficiently treat a number of medical ailments, including:
- Pain
- Parkinson’s disease
- Epilepsy
- Heart disease
- Depression
- Acne
- Psoriasis
- Multiple Sclerosis or M.S.
- Broken bones
- Bacterial infections
- Dyskinesia
- Inflammation
- Mad cow disease
- Rheumatoid arthritis
- ADHD
- Substance abuse and withdrawals
- Schizophrenia
CBD can help supplement the naturally occurring endocannabinoids with cannabinoids from the hemp plant. To check out some supplements and products we suggest visiting sites from companies like Botanicam. There you could find products which will stimulate your endocannabinoid system to create and maintain homeostasis. Additionally, CBD prevents the enzymes in your body from disintegrating the endocannabinoids produced by your body. Therefore, your body is able to retain most of the endocannabinoids, and your ECS can function adequately by itself.
Bottom Line
CBD is a great supplement that can assist your body’s endocannabinoid system to perform accurately when it is unable to do so by itself. The reason is that CBD is able to work efficiently with the body without interfering with its normal functioning. CBD is similar to the endogenous cannabinoids produced naturally by your body, and they are able to influence the receptors without getting attached directly to them. This makes CBD a natural, safe, and effective solution to assist your body in creating and maintaining homeostasis.






